Enterprise Structure in SAP
SAP enterprise structure is organizational structure that represents an enterprise in SAP R/3 system. It consists of some organizational units which, for legal reasons or for other specific business-related reasons or purposes are grouped together. Organizational units include legal company entities, sales offices, profit centers, etc. Organizational units handle specific business functions. Organizational units may be assigned to a single module (such as a sales organization assigned to Sales and Distribution (SD) module, or to several modules (such as a plant assigned to Materials Management (MM) and Production Planning (PP) module).
Enterprise Structure of SAP MM, PM and Other Modules
Enterprise structure defines various levels in an organization. These levels are placed according to some hierarchy. Each level has some specific functionality associated with it, which in a combined way describes the working of an organization. Also enterprise structure defines various organizational units that are present in an enterprise.
The Organizational Structure in FICO consists of following Organizational Levels:
- Client
- Company Code
- Chart Of Accounts
- Credit Controlling Area
- Profit Center
The Organizational Structure in MM consists of following Organizational Levels:
- Plant
- Storage Location
- Purchasing Organization
- Purchasing Group
The Organizational Structure in PM consists of following Organizational Levels:
- Planning Plant
- Maintenance Planning Plant
The Organizational Structure in SD consists of following Organizational Levels:
- Sales Organization
- Distribution Channel
- Division
- Sales Area
- Delivering Plant
- Sales Office
- Sales Group
- Shipping Point
- Sales Persons
The Organizational Structure in HCM (HR) consists of following Organizational Levels:
- Personnel Area
- Personnel Sub-Area
- Employee Group Employee
- Sub-Group etc.
The fundamental explanation of Different Organization Units is as follows
Client :
Client is a commercial Organizational Unit in R/3 System. According to the hierarchy, Client is at highest level in SAP system. Data is maintained at client level is valid for all organization level. From a business perspective, the client forms a corporate group.
Examples of Client-specific data includes:
- User Master data- such as parameters, authorization, and user groups
- Customizing data-such as organizational units, assignments, and document types
- Application data- such as business transaction data and material master data
- A client is assigned a unique three-character key.
Company:
A company is an organizational unit in Accounting which represents a business organization according to the requirements of commercial law in a particular country
Example Data :
Sl. No. Company Description
01 BICL BICL Group of Companies
Company Code:
Company Code is the Organizational Unit of Financial Accounting for which a complete self-contained set of accounts can be drawn up for purposes of external reporting. This includes recording of all relevant transactions and generating all supporting documents required for financial statements. At each Company Code level Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Account and all financial statements(Cash Flow Statement, Statement of changes in Equity, Statement of Financial Position, Related notes to the Financial Statement )can be generated. Statements Required for Legal Reporting can be generated / balanced at Company Code level. At each country level, Financial Reports need to be generated, when defining company codes, Country specific Company Codes need to be generated.
Example Data :
Sl. No. Company Code Description
01 7000 BICL Industries Ltd.
Credit Controlling Area :
Credit Controlling Area is a Financial Accounting organizational unit to monitor the Credit Limit to Customers. This organizational unit is either a single company code or, if credit control is performed across several company codes, multiple company codes. Credit information can be made available per customer within a credit control area.
Example Data :
Sl. No. Sales Org. Credit Control Area Description
01 7000 7000 BICL Industries Ltd.
Chart of Accounts :
Chart of Account contains list of General Ledger Accounts. A classification scheme consisting of a group of general ledger (G/L) accounts. A chart of accounts provides a framework for the recording of values to ensure an orderly rendering of accounting data. The G/L accounts it contains are used by one or more company codes. For each G/L account, the chart of accounts contains the account number, the account name, and technical information. A chart of accounts must be assigned to each company code. This chart of accounts is the operative chart of accounts and is used in both financial accounting and cost accounting.
Chart of Account “BICL" –Chart of Account” is to be defined to meet the Requirements of BICL
Example Data :
Sl. No. Chart of Account Description
01 BICL BICL Group of Companies
Controlling Area
Controlling Areas is an organizational unit within an Organization. Controlling Areas is being used to represent a closed system for cost accounting purposes.
Controlling Areas is used for internal reporting purposes. Multiple Company Codes can be used same Controlling Area, to have a uniform Costing Systems in place.
All the company codes in the controlling area must use one Chart of Accounts and Fiscal Year Variant. Controlling Area “7000- BICL - Standard Hierarchy” are to be used for all Company Codes
Organizational Unit Code Description
Controlling Area 7000 BICL Industries Ltd.
Profit Center Accounting :
In profit center accounting, a standard hierarchy is defined to contain all the profit centers belonging to one controlling area. Profit Center Accounting determines the profit / loss by profit center. The profit center differs from a cost center in that the cost centers merely represent units within profit centers in which costs arise. Profit centers are entities responsible for balance of revenues and costs. Profit center accounting is a statistical accounting component. It takes transaction data posted in other components and represents it from the profit center point of view.
Example Data:
Company Code Plant Profit Center Description
7000 7000 7000 Corporate Office -BICL
7000 7010 7010 Manufacturing Plant - BICL
Plant :
A Plant is an organizational unit within a company. Plant is an organizational unit that structures the enterprise from the production, procurement, distribution and stock storage area.
Example: Production facility, Trading Office where material movements are tracked and inventory valuations are monitored.
A Plant can be one of the following types of locations:
- Manufacturing facility
- Warehouse distribution center
- Regional sales office
- Corporate headquarters
- Maintenance Plant
Sl. No. Company Code Plant Description Plant Location
01 7000 7010 BICL 1 Dhaka
02 7000 7020 BICL 2 Dhaka
Storage Locations:
Storage Location is a place where stock is kept in physically.To monitor the stock of the material it is necessary to be able to store in the system location at which materials are kept. You can do this by using storage location.
A storage location has the following attributes:
- Physical inventory is carried out at the storage location level
- There may be one or more storage locations within a plant
- A storage location has a description and at least one address
- It is possible to store material data specific to a storage location
- Stock are managed on a quantity basis only and not on a value basis at storage location level
- Storage Locations are always created for a plant
Example Data
Plant Storage Loc. Code Description
7000 HO01 Head Office
7010 GS01 General Store -1
7010 GS02 General Store - 2
7010 GS03 General Store-Logistics
7020 OS01 Old Store - 1
7020 SD01 Shed - 1
Purchasing organization:
An organizational unit responsible for procuring materials or services for one or more plants and for negotiating general conditions of purchase with vendors. The purchasing organization assumes legal responsibility for all external purchase transnational requirements
- The purchasing organization is responsible for the company's purchasing requirements.
- You can incorporate purchasing into the company structure by assigning the purchasing organization to company codes and plants. This means that you can determine whether purchasing is organized centrally or decentrally in your company. You can have a combination of both.
Plant Specific Purchasing Organization : In plant-specific procurement, a purchasing organization is responsible for procuring materials for one plant only.
Cross Plant Purchasing Organization : You can set up a cross-plant purchasing organization for each company code. This purchasing organization procures material and services for all plants assigned to the company code.
Cross Company Code Purchasing Organization : If you want to organize purchasing on a cross-company-code basis, you cannot assign a company code to the purchasing organization in Customizing. When you create a purchase order, for example, the system asks you to enter the company code for which you want to procure the material.
Example Data:
Company Purchase Organization Description
7000 1000 Import Purchase
7000 1010 Central Purchase
Purchasing group:
The purchasing organization is further subdivided into purchasing groups (buyer groups), which are responsible for day-to-day buying activities. A purchasing group can also act for several purchasing organizations.
Organizational Unit Code Description
Purchasing 100 Raw Material - Local
Purchasing 110 Raw Material - Import
Purchasing 120 Packaging Material - Local
Sales Organization :
The Sales Organization is an organizational unit within logistics that structures the company according to its sales requirements. A Sales Organization is responsible for the Sale and Distribution of Goods and Services. Each Business transaction is processed within a Sales Organization. The Sales Organization must be specified in all the SD Documents
Company Code Sales Organization Code Description
7000 7000 BICL Industries Ltd.
Distribution Channel
The distribution channel represents the channel through which saleable materials or services reach customers. Typical distribution channels include wholesale, retail and direct sales. Within a sales organization a customer can be supplied through several distribution channels
Sales Organization Distribution Channel Description
7000 10 Dealer/ Distributor
7000 20 Corporate / Institutional
Division
A division can be defined as a Product group that could be made up of a wide-ranging spectrum of products. This entity normally groups together saleable materials and services for the purpose of responsibility and analysis.
Example Data
Sl. No. Division Description
01 00 Common Division
02 10 Gas Cylinder
03 20 Power Generator
Sales Area
A Sales Area can be defined as a combination of Sales Organization, Distribution Channel and Division for which each transaction is carried out. Example :
Sales Org. Distribution Channel Division
1000 10 10
1000 20 10
1000 30 10
Delivering Point / Shipping Point
A Shipping Point can be defined as a physical location (ex – a warehouse or a collection of loading ramps) from which the item is shipped for delivery.
Example Data
Sl. No. Sales Org. Plant Shipping Point Shipping Point Desc Shipping Point Location
1 1000 1010 1010 ABC 1 Narayanganj
2 2000 2010 2010 ABC 2 Dhaka
3 3000 7010 7010 ABC 3 Gazipur
Sales Office
Geographical aspects of the organizational structures in business development and sales are defined using sales offices. A sales office can be viewed as an actual office or perhaps a territory or region. Sales offices are assigned to sales areas.
Example Data
Sl. No. Sales Office Description
01 1000 BICL Industries Ltd.
Sales Groups
Sales Group Code
Dhaka A01 – A99
B01 – B99
C01 – C99
D01 – D99
Chittagong
F01 – F99
G01 – G99
H01 – H99
I01 – I99
Sylhet
J01 – J99
K01 – K99
Rajshahi
L01 – L99
M01 – M99
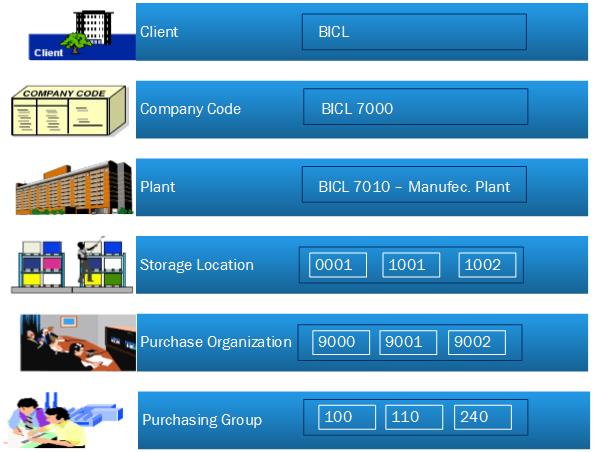
MM Enterprise Structure Sample Diagram :